Part One: Gun Violence Prevention
Reducing the risk.

Executive Summary
The prevention section of the NEA School Gun Violence Prevention and Response Guide highlights recommended strategies to reduce the risk and prevent the occurrence of gun violence incidents in education settings and communities. It includes taking actions to foster a positive and safe climate and limit access to firearms that could be used in acts of violence. For broader context and related recommendations, consult the other sections of this guide: Introduction, Part Two—Preparation, Part Three—Response, and Part Four—Recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Across all education settings, prevention efforts should be geared toward creating an environment that fosters trust-building, connection, and a sense of belonging for students. These efforts should include the use of trauma-informed and restorative practices.
- Educators can play a pivotal role in breaking the cycle of trauma and fostering a positive school climate, but their efforts must be supported with adequate funding and sufficient staffing.
- Promoting the adoption of gun violence-related bargaining language and administrative policy, including the creation or enhancement of health and safety committees, is another effective way to prevent gun violence.
Trauma-informed and restorative practices play a crucial role in maintaining strong connections between students, their peers, and educators within the school community. Across all education settings, prevention efforts are geared toward creating an environment that fosters trust-building and a sense of belonging for students.
Combating feelings of isolation and alienation among students relates directly to preventing gun violence because the majority of Pre-K–12 and higher education shooters maintained some level of affiliation with their educational institutions. Individuals who carried out a mass shooting in a Pre-K–12 school often exhibited behaviors of concern in advance, and 75 percent of the time at least one person, often a peer, was aware of the plan.1National Threat Assessment Center. (2019). Protecting America’s Schools: A U.S. Secret Service Analysis of Targeted School Violence. Retrieved February 14, 2024, from https://www.secretservice.gov/sites/default/files/2020-04/Protecting_Americas_Schools.pdf; Violence Prevention Project. (n.d.). Key Findings. Retrieved February 18, 2024, from Violence Prevention Project: https://www.theviolenceproject.org/key-findings/.
Educators can play a pivotal role in breaking the cycle of trauma and fostering a positive school climate. Recognizing warning signs, having resources to address students’ mental health and emotional needs, and ensuring that racial profiling does not take place in the process are crucial to preventing gun violence in education settings. To achieve these goals, adequate funding and sufficient staffing must be available. Recognizing the warning signs is only a part of the solution; reducing access to guns is also critical.
This section also includes recommendations for the broader community. Anonymous reporting systems have demonstrated effectiveness, providing students and other community members with a trusted avenue to raise concerns related to student wellness and safety. These systems also serve as alerts for mental health professionals regarding interpersonal violence and suicide risks.
Considering that 4.6 million children under the age of 18 live in homes with guns, secure storage interventions play a critical role in overall school safety.2Miller, M., & Azrael, D. (2022, February 22). Firearm Storage in US Households with Children: Findings from the 2021 National Firearm Survey. JAMA Network Open, 5(2), e2148823. doi:doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.48823 Additionally, community-based intervention programs offer services to students off school grounds and while traveling to and from school.
The evidence indicates that arming educators does not enhance student safety. In fact, it compromises the safe and trusting environment necessary to thwart gun violence, introducing new liability risks and complicating law enforcement responses in the event of an active shooter incident.3Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund (2024). Stop Arming Teachers. Retrieved March 14, 2024, from Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund: https://everytownresearch.org/solution/arming-teachers. In contrast, commonsense gun laws are essential for saving lives. Effective measures include:
- Require background checks on all gun sales, an approach proven to reduce gun violence;
- Pass Extreme Risk/red flag laws to provide a way for family members and law enforcement to petition a court to remove firearms from a person at risk of causing harm without a criminal proceeding;
- Pass secure firearm storage laws to prevent unauthorized access by children by requiring gun owners to lock up their firearms, which has been shown to prevent unintentional shootings and firearm suicides;
- Raise the age to purchase semi-automatic firearms to 21 to prevent potential younger shooters from easily obtaining such firearms;
- Prohibit guns on college campuses where legally viable to do so; and
- Prohibit assault weapons and high-capacity magazines, which allow shooters to fire more rounds over a short period of time and inflict more gunshot wounds during an attack.
Promoting the adoption of gun violence-related collective bargaining language and administrative policy, including the creation or enhancement of health and safety committees, is another effective way to combat gun violence. Bargaining language and administrative policy also offer important opportunities to enhance mental health supports and professional development on topics including trauma-informed crisis intervention and restorative practices.
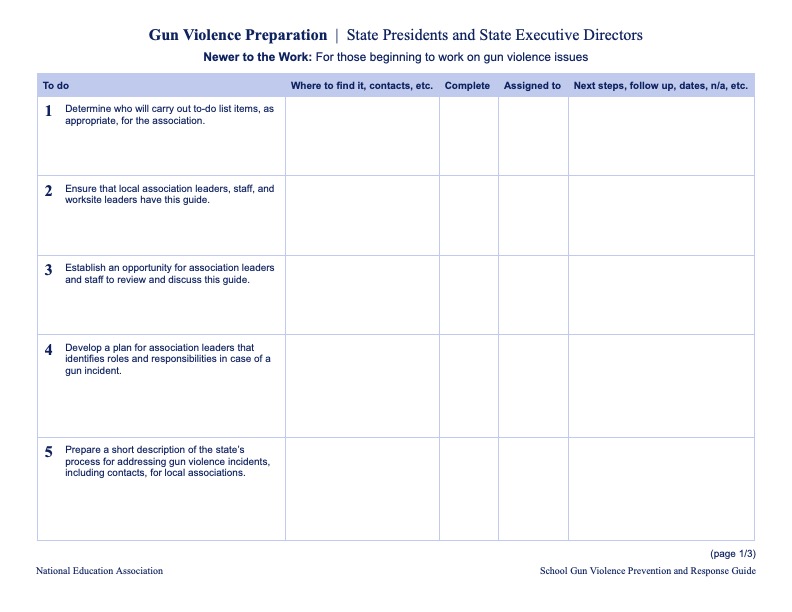
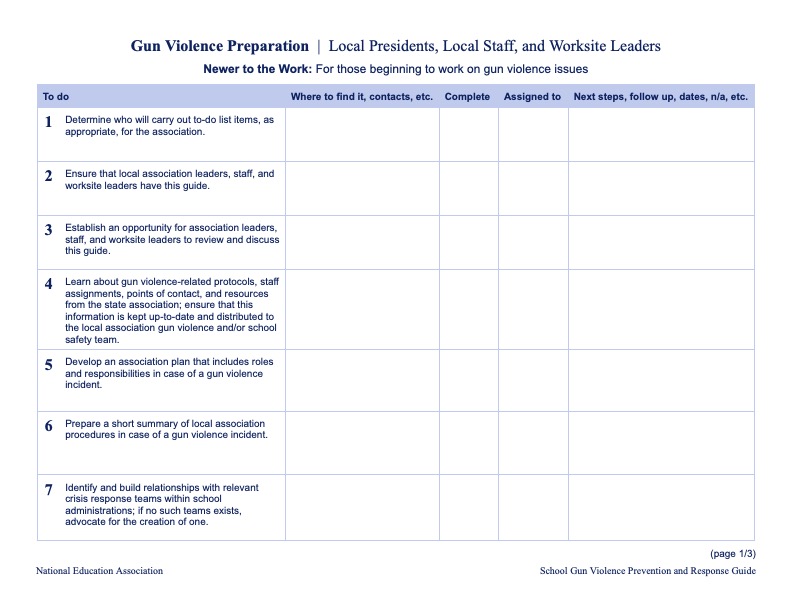
Prevention Checklists for State and Local Affiliates
These checklists can be downloaded and used to help guide state and local affiliates as they develop their own gun violence prevention and response plans.
Background
According to the American Psychological Association, “A complex and variable constellation of risk and protective factors makes persons more or less likely to use a firearm against themselves or others. For this reason, there is no single profile that can reliably predict who will use a gun in a violent act. Instead, gun violence is associated with a confluence of individual, family, school, peer, community, and sociocultural risk factors that interact over time during childhood and adolescence.”4American Psychological Association. (2013). Gun Violence: Prediction, Prevention, and Policy. Retrieved February 17, 2024, from https://www.apa.org/pubs/reports/gun-violence-prevention.
Given this complexity, taking meaningful actions to keep our students, educators, and surrounding communities safe must begin from an understanding of four key facts about gun violence in education settings.
Four Key Facts About Gun Violence in Education Settings
-
Shooters Often Have a Connection to the Pre-K–12 School or Institution of Higher Education
In the Everytown for Gun Safety’s Gunfire on School Grounds database, 60 percent of school-age shooters were current or former students of the Pre-K–12 school, including all shooters involved in mass shootings and nearly all in self-harm incidents (96 percent) and unintentional discharges of a gun (91 percent).1Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2022). How to Stop Shootings and Gun Violence in Schools. Retrieved February 17, 2024, from https://everytownresearch.org/report/how-to-stop-shootings-and-gun-violence-in-schools/. For example, Everytown analyzed the New York City Police Department’s review of active shooter incidents in K–12 schools over the five-decade period from 1966 to 2016, finding that in 3 out of 4 of these incidents, the shooter or shooters were school-age and were current or former students.2New York City Police Department. (2016). Active Shooter: Recommendations and Analysis for Risk Mitigation. Retrieved February 17, 2024, from https://www.nyc.gov/assets/nypd/downloads/pdf/counterterrorism/active-shooter-analysis2016.pdf. Similarly, the Violence Prevention Project found 89 percent of shooters at colleges and universities had a connection to the institution.3Violence Prevention Project. (n.d.). Key Findings. Retrieved February 18, 2024, from Violence Prevention Project: https://www.theviolenceproject.org/key-findings/. These data suggest the need for comprehensive strategies that combine prevention, mental health support, and crisis response to effectively tackle school gun violence.
-
Guns Discharged in Pre-K–12 Schools Generally Come from the Home of a Parent or Close Relative
School-age shooters generally do not purchase the weapon or weapons used. In a study of targeted K–12 school violence from 2008 to 2017, the U.S. Secret Service noted that 3 out of 4 shooters acquired their firearm from the home of a parent or close relative.1National Threat Assessment Center. (2019). Protecting America’s Schools: A U.S. Secret Service Analysis of Targeted School Violence. Retrieved February 14, 2024, from https://www.secretservice.gov/sites/default/files/2020-04/Protecting_Americas_Schools.pdf. This was the case, for example, with the Oxford High School shooting on November 30, 2021, in Michigan.2Albeck-Ripka, L., & Kasakove, S. (2021, December 19). What We Know About the Michigan High School Shooting. The New York Times. Retrieved February 14, 2024, from https://www.nytimes.com/article/oxford-school-shooting-michigan.html.
-
There Are Nearly Always Warning Signs
Warning signs of school shootings, if appropriately identified, can offer an opportunity for intervention beforehand. However—as discussed in more detail in the sections that follow on trauma-informed intervention practices and restorative disciplinary practices—identifying and intervening based on advanced indicators is essential but must be done without perpetuating adverse racial stereotypes, targeting those that demonstrate behavioral concerns, or compromising the trust and emotional safety of a school environment.
The U.S. Secret Service study of targeted school violence from 2008 to 2017 found that 100 percent of the perpetrators showed behaviors of concern and 77 percent of the time at least one person—most often a peer—knew about their plan.1National Threat Assessment Center. (2019). Protecting America’s Schools: A U.S. Secret Service Analysis of Targeted School Violence. Retrieved February 14, 2024, from https://www.secretservice.gov/sites/default/files/2020-04/Protecting_Americas_Schools.pdf. In the higher education context, about 44 percent of people who perpetrated mass shootings had communicated their intent in advance.2Peterson, J., & et al. (2021). Community of Intent to Do Harm Preceding Mass Public Shootings in the United States, 1966-2019. JAMA Network Open, 4(11). doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.33073.
These data suggest that fostering a trusting and emotionally safe climate where students are willing to ask adults for help and report any statements and behaviors of concern, such as gun threats on social media or weapons carrying, can be effective tools for prevention. Addressing warning signs and taking immediate action while also ensuring that racial profiling is never supported or permitted is essential.
The Sandy Hook Elementary School shooting on December 14, 2012, in Connecticut, underscores the importance of intervening when possible to stop violence before it happens. The official investigation revealed that there were several instances of the shooter’s prior behavior that were concerning. For example, when the shooter was in seventh grade, a teacher reported that “his writing assignments obsessed about battles, destruction and war, far more than others his age. The level of violence in the writing was disturbing.”3Sedensky, S. J. (2013). Report of the State’s Attorney for the Judicial District of Danbury on the Shootings at Sandy Hook Elementary School and 36 Yogananda Street, Newtown, Connecticut on December 14, 2012. Retrieved February 17, 2024, from https://schoolshooters.info/sites/default/files/Official_Sandy_Hook_Report.pdf.
-
Gun Violence in U.S. Schools Disproportionately Affects Students of Color
In the shooting incidents where the Everytown Support Fund was able to identify the racial makeup of the student body, 2 out of 3 incidents occurred in majority-minority schools.1Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2022). How to Stop Shootings and Gun Violence in Schools. Retrieved February 17, 2024, from https://everytownresearch.org/report/how-to-stop-shootings-and-gun-violence-in-schools/. Although Black students represent approximately 15 percent of the total K–12 school population in the United States,2National Center for Education Statistics, U.S. Department of Education. (2020, September). State Nonfiscal Survey of Public Elementary and Secondary Education, 1998-99 Through 2018-19; National Elementary and Secondary Enrollment by Race/Ethnicity Project Model,1972 Through 2029, Common Core Data (CCD). Retrieved February 17, 2024, from National Center for Education Statistics: https://nces.ed.gov/programs/digest/d20/tables/dt20_203.60.asp?current=yes. they make up 30 percent of the average population at schools that have been affected by a fatal shooting.3Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2022). How to Stop Shootings and Gun Violence in Schools. Retrieved February 17, 2024, from https://everytownresearch.org/report/how-to-stop-shootings-and-gun-violence-in-schools/. While perpetrators of mass shootings in schools have tended to be White, and mass shootings are often portrayed in media coverage as occurring predominantly in schools with a majority of White students, gunfire on school grounds disproportionately affects students of color.
Adverse Childhood Experiences, Childhood Trauma, Grief, and Toxic Stress
Gun violence—in a community, a home environment, or an education setting—can be a factor that produces trauma and stress for children and adults. A 2021 analysis of mass shooting data showed that a majority of mass shooters experienced early childhood trauma and exposure to violence at a young age and had an identifiable grievance or crisis event.5Shahid, S., & Duzor, M. (2021, June 1). VOA Special Report: History of Mass Shooters. Voice of America News. Retrieved February 22, 2024, from https://projects.voanews.com/mass-shootings/. NEA’s website provides additional information on toxic stress and trauma. Therefore, it is important to understand the potential impact of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) and toxic stress when addressing an incident of gun violence. Educators can play a pivotal role in breaking the cycle of trauma through early detection and focused support. To achieve this goal, state legislatures must fully fund and staff schools so that educators have the time and attention to recognize early warning signs and take action to address students’ needs.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 64 percent of adults in the United States reported having at least one type of adverse childhood experience (ACE) before the age of 18. The CDC also noted that ACE events are typically the result of violence, abuse, neglect, and environmental factors that expose children to substance use, mental health-related issues, and parental separation.6Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.). Fast Facts: Preventing Adverse Childhood Experiences. Retrieved February 22, 2024, from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: https://www.cdc.gov/violenceprevention/aces/fastfact.html.
Trauma occurs when someone feels threatened by serious harm, whether it is physical, mental, or emotional. While not all ACEs lead to childhood trauma, people who suffer from one or more such adversities may experience a negative impact on their overall well-being, education, and career. Researchers have found that trauma can change the brain and the body’s makeup, which can lead to diseases like obesity, heart disease, diabetes, asthma, and mental health disorders.7Center for Substance Abuse Treatment. (2014). Chapter 3. Understanding the Impact of Trauma. In Trauma-Informed Care in Behavioral Health Services (Vols. Treatment Improvement Protocol, No. 57). Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Retrieved February 22, 2024, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK207191/. Neuropsychologists have found that traumatic experiences can, in fact, alter a child’s brain, activating its “fight, flight, or freeze” responses and reducing the areas where learning, especially in regard to language, occurs. When this shift happens repeatedly, it fundamentally changes the brain, particularly for children under the age of 5, to adapt and survive under the worst conditions.8Flannery, Mary Ellen. (2016, May 17). How Trauma Is Changing Children’s Brains. NEA Today. Retrieved February 18, 2024, from NEA Today: https://www.nea.org/nea-today/all-news-articles/how-trauma-changing-childrens-brains.
The ongoing presence of ACEs may also contribute to toxic stress. The American Academy of Pediatrics defines “toxic stress” as prolonged or significant adversity in the absence of mitigating social-emotional buffers, such as a supportive adult. This kind of persistent activation of the stress response systems can result in a wide array of biological changes that occur at the molecular, cellular, and behavioral levels; disrupt the development of brain architecture; and increase the risk for stress-related disease and cognitive impairment well into adulthood.9Garner, A., & Yogman, M. (2021, August). Preventing Childhood Toxic Stress: Partnering with Families and Communities to Promote Relationship Health. Pediatrics, 148(2), e2021052582. https://publications.aap.org/pediatrics/article/148/2/e2021052582/179805/Preventing-Childhood-Toxic-Stress-Partnering-With?autologincheck=redirected.
Experiencing adversity, including trauma and toxic stress, can significantly shape an individual’s health and life outcomes. Childhood trauma can also negatively affect the mental health of and educational outcomes for higher education students.10Lecy, N., & Osteen, P. (2022). The Effects of Childhood Trauma on College Completion. 63, 1058-1072. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11162-022-09677-9; Assari, S., & Landarani, M. M. (2018). Violence Exposure and Mental Health of College Students in the United States. Behavioral Sciences, 8(6), 53. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/bs8060053.
Many other factors have been proven to cause toxic stress, including poverty, racism, bullying, community violence, and generational (historical) trauma.11Cronholm, P., & et al. (2015, September). Adverse Childhood Experiences Expanding the Concept of Adversity. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 49(3), 354-361. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2015.02.001; Garner, A., & Yogman, M. (2021, August). Preventing Childhood Toxic Stress: Partnering with Families and Communities to Promote Relationship Health. Pediatrics, 148(2), e2021052582. https://publications.aap.org/pediatrics/article/148/2/e2021052582/179805/Preventing-Childhood-Toxic-Stress-Partnering-With?autologincheck=redirected. According to researchers at the Center for the Developing Child at Harvard University, ACEs-generated trauma includes community and systemic threats from inside or outside the home environment because the brain recognizes a present threat and goes on high alert.12Center on the Developing Child. (2020, October 30). ACEs and Toxic Stress: Frequently Asked Questions. Retrieved from Center on the Developing Child at Harvard University: https://developingchild.harvard.edu/resources/aces-and-toxic-stress-frequently-asked-questions/.
Childhood bereavement can also have a significant impact on children’s health and well-being. “The death of someone close to a child has a profound and lifelong effect on the child and may result in a range of both and short and long-term reactions.”13Schonfeld, D. J., & Demaria, T. (2016). Supporting the Griefing Child and Family. Pediatrics. Retrieved June 10, 2024, from https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-2147. Schools can learn more about the impact of bereavement and becoming grief-sensitive schools to better support student learning and development. Organizations, such as The Coalition to Support Grieving Students, provide resources to assist schools in becoming grief-sensitive.
Debunking Myths and Misconceptions About Gun Violence
Myth
The only way to stop a “bad guy” with a gun is a “good guy” with a gun.
Fact
If more guns everywhere made us safer, the United States would be the safest country in the world. Instead, we have a gun homicide rate 26 times that of other high-income countries.1Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2023). Gun Violence in America. Retrieved March 14, 2024, from https://everytownresearch.org/report/gun-violence-in-america/.
Myth
I don’t own a gun, so I don’t need to worry about my kids getting ahold of one.
Fact
More than 60 percent of unintentional gun deaths among children involve a gun belonging to a family member of the shooter.1Wilson, R. F. (2023). Unintentional Firearm Injury Deaths Among Children and Adolescents Aged 0–17 Years — National Violent Death Reporting System, United States, 2003–2021. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), 72(50), 1338-1345. In the United States, 4.6 million children under the age of 18 live in a household with at least one loaded, unsecured gun,2Miller, M., & Azrael, D. (2022, February 22). Firearm Storage in US Households with Children: Findings from the 2021 National Firearm Survey. JAMA Network Open, 5(2), e2148823. doi:doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.48823 but research also suggests that school shooters under the age of 18 predominantly obtain their guns from family, relatives, or friends.3Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2022). How to Stop Shootings and Gun Violence in Schools. Retrieved February 17, 2024, from https://everytownresearch.org/report/how-to-stop-shootings-and-gun-violence-in-schools/. As a result, children may be able to get ahold of a gun even if no one in their household owns one.
Myth
Arming educators will keep our kids safer.
Fact
Research suggests that the presence of a gun may potentially increase the risks posed to children. Many school safety experts and law enforcement groups oppose arming teachers, as does the NEA.1Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2024-d). Stop Arming Teachers. Retrieved March 14, 2024, from Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund: https://everytownresearch.org/solution/arming-teachers. Law enforcement officers receive hundreds of hours of training in areas including firearm proficiency and active shooter response. Training requirements for educators are often a fraction of the training hours required by police officers.
Myth
Criminals will always find a way to get their hands on a gun.
Fact
Laws like background checks stop gun sales to people legally prohibited from buying guns. This includes people with felony convictions, domestic abuse restraining orders, and others. Since 1994, these laws have blocked more than 4 million gun sales to people who could not legally own guns.1Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2024-h). Background Checks on All Gun Sales. Retrieved March 14, 2024, from Everytown for Gun Safety: https://www.everytown.org/solutions/background-checks/; Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2021-c). Undeniable: How Long-Standing Loopholes in the Background Check System Have Been Exacerbated by COVID-19. Retrieved March 14, 2024, from https://everytownresearch.org/report/background-check-loopholes/.
Prevention Strategies
Education settings at all levels must establish safe, supportive, nurturing environments where students can thrive. Strategies including trauma-informed crisis intervention programs and active engagement with students and their families are essential to gun violence prevention. In addition, community violence intervention programs that integrate mental health and emotional supports help address the systemic and underlying factors that can lead to gun violence.
Foster Safe and Supportive School Climates
When schools are adaptable to the needs of their students, educators, families, and community, they can provide students with care and compassion and create conditions that prevent shootings and other violence. For example, a community school that has high levels of violence inside or outside the school building may fund programs that create safe walking and transportation routes to and from school, often referred to as safe passage; grant alternatives to out-of-school suspensions that offer meaningful educational opportunities for students; provide family counseling; increase access to mentoring, both inside and outside of school; and incorporate restorative justice into disciplinary policies. NEA’s website includes additional information on community schools.
Students are often the first to notice signs that a peer is in crisis, has brought a weapon to school, or has shared plans to commit a violent act; however, they are sometimes reluctant to share these observations—or their own personal struggles and needs—with adults they do not trust. Students may be reluctant to relay information that might help avert a gun violence incident because of fear of getting in trouble, being labeled a “tattletale,” or not being believed or taken seriously. A pre-established relationship of trust with at least one educator increases students’ willingness to report potential incidents or identify bullying or violence they experience or witness.14Volungis, A. M., & Goodman, K. (2017). School Violence Prevention: Teachers Establishing Relationships with Students Using Counseling Strategies. Sage Open, 7(1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244017700460.
Many education support professionals (ESPs) live in the same community as their students and are often trusted confidants; they play a key role in the preventative and intervention actions. ESPs—including, but not limited to, custodial and maintenance, food service, clerical, security, and transportation professionals—are often the first to confront a shooter. Indeed, almost half of NEA ESP members—48 percent—spend a great deal of their time promoting school safety. The job responsibilities of another 28 percent are somewhat related to promoting such work.
To build trust, educators must have cultural competency to counteract unconscious bias and reduce the risk of biased decision-making that can impede a student’s ability to trust them.
An all-staff activity called Know Me, Know My Name is an example of an effective way to identify students who may need support but go unseen.15Illinois Education Association. (n.d.). Retrieved from Know Me, Know My Name: https://ieanea.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Know-me-know-my-name-plan-1.pdf. Low-cost and relatively simple, the activity helps educators identify children who may need adult intervention via outreach and relationship-building, encompassing the ideals of safe, stable, and nurturing relationships (SSNR). SSNRs help interrupt cycles of violence and reduce the impact of students’ exposure to abuse and neglect. The Harvard School of Education also developed relationship mapping, which is another example of this type of activity.16Harvard Graduate School of Education. (n.d.). Retrieved from Relationship Mapping Strategy: https://mcc.gse.harvard.edu/resources-for-educators/relationship-mapping-strategy.
The Importance of Connections in Higher Education
Compelling evidence indicates that students at institutions of higher education who felt connected to individual staff and/or faculty experienced multiple positive outcomes, including those related to emotional well-being. Students are also less likely to experience substance and alcohol use and have better health outcomes. Connectedness is especially crucial for first-year students; perceived decreases (from high school) in social connectedness can lead to heightened feelings of loneliness and anxiety. These positive connections had little to do with an educator’s teaching style or pedagogy but with their ability to care about their students as people.1Morgan, E., & et al. (2014). The School Discipline Consensus Report: Strategies from the Field to Keep Students Engaged in School and Out of the Juvenile Justice System. U.S. Department of Justice, Office of Justice Programs. Retrieved March 14, 2024, from https://www.ojp.gov/library/publications/school-discipline-consensus-report-strategies-field-keep-students-engaged.
Implement Trauma-Informed and Grief-Sensitive Crisis Intervention and Restorative Disciplinary Practices
Students who commit acts of gun-related violence in schools almost always have shown warning signs that concerned other people around them.17National Threat Assessment Center. (2019). p. 58, Protecting America’s Schools: A U.S. Secret Service Analysis of Targeted School Violence. Retrieved February 14, 2024, from https://www.secretservice.gov/sites/default/files/2020-04/Protecting_Americas_Schools.pdf. Therefore, identifying students who may need support to prevent a crisis from becoming violent while ensuring that racial profiling and other biased actions are neither supported nor permitted is key to preventing gun violence in schools.
To respond to signs of distress in a manner that serves students and protects the community, schools can convene a multidisciplinary team that uses trauma-informed and grief-sensitive crisis intervention practices in collaboration with other community partners. A School Improvement Team, Resilience Team, Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS) Team, or other such entities that may already exist could potentially serve this function. Whatever its name, such a team would receive information about a student who may be in crisis, evaluate the situation, design interventions to prevent violence, and provide appropriate in-school engagement, support, and resources. Every team that addresses crisis intervention should include ESPs; however, ESP membership must be voluntary. Every school community is different, so team structures and functions must be designed and implemented based on the unique needs of the student body and the broader school community.
Behavioral threat assessments are frequently used to identify students who are at risk of committing violence and get them the help they need. These programs generally consist of multidisciplinary teams that are specifically trained to intervene at the earliest warning signs of potential violence and divert those who would do harm to themselves or others to appropriate treatment. NEA opposes “behavioral threat assessment programs and approaches that disproportionately target Native students and students of color.”18NEA. (2023). Legislative Program. Reference I.E.41. Retrieved from https://www.nea.org/about-nea/governance-policies/nea-legislative-program. The Association urges all school community members to be prepared to ensure that if they use behavioral threat assessments, they achieve their desired outcomes without adverse racial impact. If such assessments are in use, they must be properly resourced, including with release time for the counselors, nurses, or other educators who serve on a team conducting behavioral threat assessments.
NEA does not believe that the criminalization and over-policing of students is the right approach to addressing gun violence in education settings. Research shows that exclusionary discipline programs, including zero-tolerance policies, disproportionately impact students of color and contribute to the school-to-prison pipeline, including through their subjective application toward students of color.19Ford, S. (2021). Learning While Black: How “Zero Tolerance” Policies Disproportionately Affect Black Students. University of Florida Journal of Law & Public Policy, 32(1), 49-70. Retrieved February 22, 2024. Zero-tolerance policies and harsh disciplinary practices result in negative academic outcomes for students given that school suspensions are a stronger predictor of dropping out of school than grade-point average and socioeconomic status.20Suh, S., & Suh, J. (2007). Risk Factors and Levels of Risk for High School Dropouts. Professional School Counseling, 10(3). doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/2156759X0701000312. Furthermore, a longitudinal study done with children ages 9 and 10 found that “enforcing these kinds of disciplinary actions can impair typical childhood development, leading to academic failure, student dropout, and emotional and psychological distress, disproportionately affecting Black children, multiracial Black children, and children from single-parent homes.21Fadus, M., & et al. (2021, August). Racial Disparities in Elementary School Disciplinary Actions: Findings from the ABCD Study. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychology, 60(8), 998-1009. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2020.11.017.
By contrast, NEA emphasizes the use of behavioral practices centered in restorative justice and the elimination of inequitable policies, practices, and systems that disproportionately harm Native People and People of Color—including those who are LGBTQ+, have disabilities, and/or are multilingual learners—and deprive many students of future opportunities. Trauma-informed prevention strategies should include restorative-based practices.
Investing in Restorative Practices
Restorative practices are based on values that holistically prevent and repair harm, build community and relationships, and result in a positive, supportive school climate. Schools that increased the use of restorative practices saw a decrease in schoolwide misbehavior, substance use, and student mental health challenges as well as improved school climate and student achievement. A key recommendation from the Learning Policy Institute is to invest in ongoing education and support for all educators to develop knowledge of and expand access to restorative practices among all students.1Darling-Hammond, S. (2023, May 24). Fostering belonging, transforming schools: The impact of restorative practices. Retrieved March 14, 2024, from Learning Policy Institute: https://learningpolicyinstitute.org/product/impact-restorative-practices-brief.
Engage School Communities in Gun Violence Prevention Efforts
School safety requires all stakeholders—students, families, educators, educators’ unions, mental health professionals, law enforcement professionals, organizations promoting racial and social justice, and community members—to collaborate and work together.
Here are examples of how to engage students and families in gun violence prevention:
- Create a safety reporting program. These programs should ensure all students, families, educators, and community members are aware of the reporting system so that they have a trusted avenue to raise concerns when issues of student wellness or safety arise. In a four-year study of the Say Something Anonymous Reporting System (SS-ARS) in a school district in the southeastern United States, more than half of firearm-related tips were deemed “life safety” events, requiring an immediate response from the school team and emergency services. The SS-ARS also identified tips related to interpersonal violence and suicide concerns, which both have implications for firearm violence. Research suggests that adolescent firearm injuries often stem from interpersonal violence, and firearm use significantly escalates the risk for self-inflicted injury and suicide completion. It is imperative that awareness of such reporting systems is amplified to increase use by the community, particularly students; however, it likely requires additional investment in supports and services for adolescents to help mitigate the burden on those who respond to these tips.22Thulin, E. J., & et al. (2024). Firearm-Related Tips in a Statewide School Anonymous Reporting System. Pediatrics, 153(2), e2023063861. doi:https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2023-063861. State initiatives—like Utah’s SafeUT crisis chat and tip line, which is used in almost all K–12 schools and some institutions of higher education in the state, by the Utah National Guard, and with first responders and their families—can also serve this function.23SafeUT. (n.d.). Retrieved from SafeUT: https://safeut.org/. In higher education contexts, there are greater restrictions on how schools can communicate with parents and families than in elementary, middle, and high schools.
- Help families start conversations with their school community. When families communicate openly, honestly, and directly with school officials, educators, and administrators, they can help prevent gun violence. Stand with Parkland developed the resource “5 Questions Every Family Should Ask as the School Year Begins” to assist families in ensuring their children’s safety and better understand how prepared a school is to address safety issues.24Stand with Parkland. (n.d.). Retrieved from 5 Questions Every Family Should Ask as the School Year Begins: https://standwithparkland.org/5-questions/.
- Use strategies that encourage effective communication on difficult topics. The NEA Health and Safety Program partnered with the Right Question Institute and the Brown School of Public Health to provide a training module to help support families, educators, and students effectively communicate around health and safety issues. The Association also produced a training module—Pathways for Effective School-Family Partnerships: A Strategy for Productive School Health and Safety Dialogue. This training is based on the Right Question Institute’s Question Formulation Technique (QFT), a structured method for generating and improving questions that can be used by individuals or groups.
Promote Secure Storage Practices to Keep School Communities Safe
Evidence strongly suggests that secure firearm storage—storing guns unloaded, locked, and separated from the ammunition—is essential to any effective strategy to keep students, educators, schools, and communities safe.25Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2023, May 26). Preventable Tragedies: Unintentional Shootings by Children. Retrieved from Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund: https://everytownresearch.org/report/notanaccident/. One study showed that the majority of children are aware of where their parents store their guns. More than one-third of those children reported handling their parents’ guns, many doing so without the knowledge of their parents.26Baxley, F., & Miller, M. (2006). Parental Misperceptions About Children and Firearms. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 160(5), 542-547. doi:doi:10.1001/archpedi.160.5.542.
Secure storage not only decreases the likelihood of gun violence on school grounds, but it also reduces firearm suicide rates. A recent study of two decades of suicide prevention laws showed that the rate of gun suicide among young people ages 10 to 24 years old was lower in 2022 than in 1999 in states with the most protective secure gun storage laws, which hold gun owners accountable for failing to store their firearms securely. In states with no secure storage laws or only reckless access storage laws, the gun suicide rate among young people ages 10 to 24 years old increased by 36 percent from 1999 to 2022.27Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2023-h). Two Decades of Suicide Prevention Laws: Lessons from National Leaders in Gun Safety Policy. Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. Retrieved from https://everytownresearch.org/two-decades-of-suicide-prevention-laws-lessons-from-national-leaders-in-gun-safety-policy/.
In states where colleges and universities are required to allow firearms on campus, schools should encourage students to securely store their firearms.
The Value of Trauma-Informed Practices
Researchers have defined trauma-informed practices (TIP) as a set of approaches that address the impact of trauma by creating a safe and caring environment. TIP includes restorative practices and a focus on creating a safe school culture, building relationships, and supporting students’ self-efficacy. When effectively implemented, these practices can reduce instances of bullying and aggression, improve achievement, increase self-esteem for students, improve connections between students and educators as well as among students, and strengthen social and emotional skills. By doing so, schools can create school climates where gun violence is less likely.1Lodi, E., & et al. (2021, December 23). Use of Restorative Justice and Restorative Practices at School: A Systematic Literature Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(1), 96. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010096.
The entire school community must receive training to successfully implement a restorative practices discipline model. Ineffective training and partial implementation can contribute to frustration and skepticism about such initiatives.
NEA’s guidance on trauma-informed practices provides a list of common actions that educators can take to implement across education settings, which include the following:
- Support students from the bus stop to the classroom (and beyond!);
- Be aware of what may upset a student;
- Show compassion, not judgment;
- Give students a safe space to share and express their feelings;
- Help students develop a growth mindset;
- Use restorative practices that minimize punitive discipline outcomes;
- Build relationships;
- Meet students where they are;
- Don’t ignore possible “warning signs”;
- Take care of yourself; and
- Encourage all educators to be trained on trauma-informed practices.
Educators can encourage a culture of secure gun storage by increasing awareness of secure storage practices. One example of an effective awareness campaign is the Everytown Support Fund’s Be SMART program, which focuses on fostering conversations with other adults about secure gun storage. Although educators may be familiar with the SMART acronym for goal-setting purposes, in this context, the acronym stands for:
- Secure guns in homes and vehicles,
- Model responsible behavior,
- Ask about unsecured guns in homes,
- Recognize the role of guns in suicide, and
- Tell your peers to be SMART.
The program’s purpose is to facilitate behavior change for adults and help parents and adults prevent child gun deaths and injuries.28Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2023, May 26). Preventable Tragedies: Unintentional Shootings by Children. Retrieved from Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund: https://everytownresearch.org/report/notanaccident/.
Schools can partner with Be SMART and pass resolutions requiring that all student households receive Be SMART information, which is already happening in Los Angeles, San Diego, and Denver, among other locations.29Sawchuk, S. (2021, December 8). More Schools Are Reminding Parents to Secure Their Guns. Education Week. Retrieved from https://www.edweek.org/leadership/more-schools-are-reminding-parents-to-secure-their-guns/2021/12. School districts across the country have taken this vital action, impacting more than 10 million students,30Everytown for Gun Safety. (2023, August 25). Press Release: As Kids Head Back to School Nationwide, What to Know about Keeping Communities Safe From Gun Violence This Upcoming School Year. Retrieved from Everytown for Gun Safety: https://www.everytown.org/press/as-kids-head-back-to-school-nationwide-what-to-know-about-keeping-communities-safe-from-gun-violence-this-upcoming-school-year/. and some institutions of higher education have partnered with the program. Be SMART’s Secure Storage Toolkit provides all the information and resources you need to encourage your school to pass a secure storage resolution.
Governors, federal and state departments of health and education, legislatures, nonprofit organizations, and local officials can also work together to develop and fund programs that increase awareness of the need to store firearms securely.31For example, see the City Gun Violence Reduction Insight Portal (CityGRIP), available at https://citygrip.org/.
Increase Mental Health and Suicide Prevention Support
Firearms are the leading cause of death among youth in the United States, and firearm suicides account for more than 4 out of 10 of these deaths. The rate of firearm suicide among young people ages 10 to 24 years old increased by 30 percent from 1999 to 2022.32Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2023-h). Two Decades of Suicide Prevention Laws: Lessons from National Leaders in Gun Safety Policy. Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. Retrieved from https://everytownresearch.org/two-decades-of-suicide-prevention-laws-lessons-from-national-leaders-in-gun-safety-policy/ Experts are sounding the alarm about young people’s mental health. A recent survey from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention found that, overall, 42 percent of teens experienced a persistent feeling of sadness or hopelessness, while 57 percent of female and 29 percent of male respondents felt that way. The same survey found that, overall, 22 percent of teens seriously considered attempting suicide, while 30 percent of female respondents and 14 percent of male respondents did.33Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). p. 63, Youth Risk Behavior Survey: Data Summary and Trends Report, 2011-2021. Retrieved March 14, 2024, from https://www.cdc.gov/healthyyouth/data/yrbs/pdf/YRBS_Data-Summary-Trends_Report2023_508.pdf. For many reasons—including the prevalence of guns in our society—the elevated risk for youth gun suicide crisis continues to rise. Furthermore, a large proportion of perpetrators of mass shootings expressed suicidal intentions, suggesting suicide prevention through crisis intervention could be a meaningful mitigating factor for mass shooting incidents.34Violence Prevention Project. (2021, November 17). Suicidality of Perpetrators. Retrieved from Violence Prevention Project; Remnick, D. (2022, May 31). What Makes a Mass Shooter? The New Yorker. Retrieved from https://www.newyorker.com/podcast/politics-and-more/what-makes-a-mass-shooter.
School-employed health professionals, who navigate the education system and the challenges of emotional and social development, serve as a critical resource for students. These professionals may be among the first to know when students are experiencing difficulties or when they are at risk of turning to violence. Unfortunately, the current national shortage of specialized school-based counselors, psychologists, sociologists, and nurses means that meeting the needs of students can be a challenge, and this challenge is often exacerbated in under-resourced communities. NEA determined in the report “Elevating the Education Professions: Solving Educator Shortages by Making Public Education an Attractive and Competitive Career Path” that solving educator shortages requires evidence-based, long-term strategies to address both recruitment and retention. The report noted that mental health positions were among the most understaffed in schools.35NEA. (2022, 10). Elevating the Education Professions: Solving Educator Shortages by Making Public Education an Attractive and Competitive Career Path. Retrieved 02 23, 2024, from https://www.nea.org/sites/default/files/2022-10/29302-solving-educator-shortage-report-final-oct-11-2022.pdf.
School-based health services, including behavioral health, provide crucial support to students. School-based Medicaid services, for example, play an essential role in the health of children and adolescents, including those related to behavioral health. With more than 41 million kids covered by Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), the school setting offers a unique opportunity to meet children where they are.36U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2023, May 18). Biden-Harris Administration Takes Action to Help Schools Deliver Critical Health Care Services to Millions of Students. Retrieved February 19, 2024, from U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: https://www.hhs.gov/about/news/2023/05/18/biden-harris-administration-takes-action-help-schools-deliver-critical-health-care-services-millions-students.html#:~:text=Medicaid%20and%20CHIP%20cover%20more%20than%20half%20of,weekly%20in%20school%20during%20mo. Schools, early childhood settings, and local education agencies help support children and their families, providing children and youth with access to important healthcare services on-site. For information on how to utilize the historic investment into school-based services by the Bipartisan Safer Communities Act, see NEA’s Your Guide to the BSCA. NEA’s website also includes guidance on bargaining and advocacy tactics to support educators’ mental health.
School-based health centers (SBHCs) can also help make quality primary care more accessible for children and adolescents.37Kjolhede, C., & et al. (2021, October 1). School-Based Health Centers and Pediatric Practice. Pediatrics, 148(4), e2021053758. doi:https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2021-053758. “School-based health care advances health equity for children and adolescents who experience barriers to accessing care because of systemic inequities, their family income, or where they live,” according to the School-Based Health Alliance. “School-based health centers, the most comprehensive type of school-based health care, do this by providing primary, behavioral, oral, and vision care where youth spend most of their time—at school.”38School-Based Health Alliance. (2024). What Is School-Based Health Care? Retrieved from https://www.sbh4all.org/what-we-do/. These organizations can collaborate with schools to support student well-being by contributing clinical expertise to supplement existing services at the school.39National Council for Mental Wellbeing. (2023). Partnering with Schools to Improve Youth Mental Health: A Resource for Community Mental Health and Substance Use Care Organizations. Retrieved from https://sbh4all.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/ParterningwithSchoolstoImproveYouthMentalHealth_2023-final.pdf.
The trauma that comes from the threat of gun violence is deeply affecting the mental health and well-being of not only students but also educators. The needs of educators are too often overlooked when resources are being offered in schools to address trauma from gun violence. There must be an increase in support and mental health resources for educators to sustain the workforce as they continue to face the threat of gun violence in schools.
Through NEA Member Benefits, NEA members receive access to the NEA Mental Health Program, powered by AbleTo, which provides 24/7 access to “evidence-backed tools for stress, anxiety, depression, or whatever you’re going through.”
The federal government’s Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) Disaster Distress Helpline offers free, 24/7 crisis counseling for people experiencing emotional distress related to any natural or human-caused disaster, including shootings. Dial or text 1-800-985-5990 to connect with counselors in more than 100 languages via third-party interpretation services.
Programs that help educators recognize the warning signs of mental health issues include Emotional CPR and Mental Health First Aid.
Help is also available for individuals who are struggling or in crisis by calling or texting 988 or chatting at 988lifeline.org. State initiatives, like SafeUT described earlier in this section, on anonymous reporting for school safety can also provide mental health support for Pre-K–12 and higher education students.
Integrate Community Violence Intervention Programs Into Schools
Community violence occurring in and around schools significantly affects students and educators. An assessment of the CDC Youth Risk Behavior Survey40Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Youth Risk Behavior Survey: Data Summary and Trends Report, 2011-2021. Retrieved March 14, 2024, from https://www.cdc.gov/healthyyouth/data/yrbs/pdf/YRBS_Data-Summary-Trends_Report2023_508.pdf. showed that witnessing community violence was linked to elevated odds of gun carrying, substance use, and suicide risk among Black, Hispanic, and White students, regardless of gender.41Harper, C., & et al. (2023, April 28). Witnessing Community Violence, Gun Carrying, and Associations with Substance Use and Suicide Risk Among High School Students — Youth Risk Behavior Survey, United States, 2021. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR) Supplements, 72(1), 22-28. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.su7201a3.
In neighborhoods that experience community violence, schools can support Community Violence Intervention (CVI) strategies to mitigate its impact on youth.42Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2024). Community-Led Public Safety Strategies. Retrieved 3 12, 2024, from https://everytownresearch.org/report/community-led-public-safety-strategies/. Examples of these programs include the following:
- Safe passage programs provide safe routes to and from schools to reduce student exposure to gun violence. To achieve this goal, educators, law enforcement groups, and communities collaboratively implement protocols and procedures to ensure student safety.43Everytown For Gun Safety Support Fund. (2024, May 24). The Impact of Gun Violence on Children and Teens. Retrieved May 24, 2024, from Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund: https://everytownresearch.org/report/the-impact-of-gun-violence-on-children-and-teens/. A longitudinal study analyzing data from 2005–2016 found that following the program’s implementation, incidents of crime along these routes dropped an average of 28 percent for simple assault and battery; there was a 32 percent reduction in aggravated assault and battery. Furthermore, overall weekday criminal incidents on school grounds decreased by an average of 39 percent per year where safe passage programs were implemented.44Sanfelice, V. (2019, August). Are safe routes effective? Assessing the effects of Chicago’s Safe Passage program on local crimes. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 164, 357-373. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167268119302033?via%3Dihub.
- School-based violence prevention programs provide students and educators with information about violence, change how youth think and feel about violence, and enhance interpersonal and emotional skills. Chicago’s Becoming a Man (BAM) program—one example of a school-based violence prevention program—has reduced juvenile justice system readmission by 80 percent.45Heller et al., S. B. (2016, August). Thinking, Fast and Slow? Some Field Experiments to Reduce Crime and Dropout in Chicago. Retrieved from National Bureau of Economic Research: https://www.nber.org/papers/w21178.
- Youth engagement and employment programs support students outside of schools.46Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2023, May 12). Summer Youth Employment Programs for Violence Prevention: A Guide to Implementation and Costing. Retrieved from Everytown for Gun Safety and Support Fund: https://everytownresearch.org/report/summer-youth-employment-programs/. These programs often center on healing or personal development. For example, The TraRon Center helps youth gun violence survivors in Washington, D.C., heal through after-school art therapy. Programs focusing on youth employment also show success. For example, a researcher found that participation in Boston’s Summer Youth Engagement Program led to a decrease in participants’ violent crime arraignments by 35 percent in the 17 months after program completion.47Modestino, A. S. (2019, Summer). How Do Summer Youth Employment Programs Improve Criminal Justice Outcomes, and for Whom? Journal of Policy Analysis and Management, 38(3), 600-628. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/pam.22138.
- Crime prevention through environmental design involves deliberate efforts to change the built environment of neighborhoods, buildings, and grounds to reduce crime and increase community safety.48Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2021). Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design. Retrieved from https://everytownsupportfund.org/report/crime-prevention-through-environmental-design/; CityGRIP. (n.d.). Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design. Retrieved January 9, 2024, from CityGRIP: Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design. https://citygrip.org/ . Programs encompass a wide variety of approaches and efforts to rehabilitate areas and discourage violence through visible signs that a community is cared for and watched over. Because gun violence is so costly and these simple fixes are not, communities save hundreds of dollars for every dollar that is invested.49Branas, Charles C., et al.. (2016, December). Urban Blight Remediation as a Cost-Beneficial Solution to Firearm Violence. American Journal of Public Health, 106(12), 2158-2164. doi:https://doi.org/10.2105/ajph.2016.303434.
Together, these programs offer services to students going to and from school and students on and off school and building grounds.
Do Not Arm Teachers or Other Educators
Arming teachers and other educators does not make schools safer; to the contrary, it escalates the risk of shootings and introduces new liability risks.50Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2024-d). Stop Arming Teachers. Retrieved March 14, 2024, from Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund: https://everytownresearch.org/solution/arming-teachers. As noted earlier in this guide, many educators, parents, and school safety experts, including several law enforcement groups, are opposed to arming teachers.
Research strongly indicates that children will access guns when guns are present, including on school grounds. There have been numerous incidents of misplaced guns in schools that were left in bathrooms,51Metrick, B. (2016, September 13). Ex-teacher charged for leaving gun in school bathroom, police say. USA Today. Retrieved from https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation-now/2016/09/13/ex-teacher-charged-leaving-gun-school-bathroom-police-say/90314614/ in locker rooms,52Associated Press. (2018, April 3). No charges after Isabella Co. sheriff accidentally leaves gun at school. Detroit Free Press. Retrieved from https://www.freep.com/story/news/local/michigan/2018/04/03/isabella-county-sheriff-gun-school/481486002/ and at sporting events.53Laine, C. (2019, January 24). Woman finds gun in bleachers at basketball tournament. WNEM. https://web.archive.org/web/20190710221102/https://www.wnem.com/news/woman-finds-gun-in-bleachers-at-basketball-tournament/article_193ee078-1ff4-11e9-841f-8f08f82a75ca.html
For more on school resource officers and policing in school, see this guide’s section on school policing. Everytown’s Students Demand Action website includes additional information on strategies to oppose arming teachers.
Advocacy-Based Prevention Strategies
Advocate for Measures That Limit Access to Guns
Gun safety policies save lives. The Everytown Support Fund’s Gun Law Rankings, which compare the gun violence prevention policies of all 50 states, show a strong correlation between a state’s gun laws and its rate of gun deaths. States with strong gun safety regulations, such as the policies outlined below, have lower rates of gun violence. States with weaker gun laws, such as no-permit carry and Shoot First laws (also known as Stand Your Ground laws), have higher rates of gun violence.54Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2024, January 4). Gun Safety Policies Save Lives. Retrieved from Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund: https://everytownresearch.org/rankings/. The following gun violence prevention policies save lives and reduce the toll of gun violence on communities:
-
Requiring background checks on all gun sales
Background checks are proven to reduce gun violence. Twenty-two states and the District of Columbia already require a background check on all handgun sales.1Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2024, January 4). Which states require background checks and/or permits to purchase handguns? Retrieved January 9, 2024, from Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund: https://everytownresearch.org/rankings/law/background-check-and-or-purchase-permit/. An Everytown Support Fund investigation showed that as many as 1-in-9 people looking to buy a firearm on this country’s largest online gun marketplace cannot legally purchase firearms—including those under the age of 18.2Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2021, February 1). Unchecked: An Investigation of the Online Firearm Marketplace. Retrieved from Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund: https://everytownresearch.org/report/unchecked-an-investigation-of-the-online-firearm-marketplace/. As part of a comprehensive plan to prevent gun violence in education settings, states and the federal government must pass laws that require background checks on all gun sales so that adolescents and people prohibited from possessing firearms cannot easily purchase them from unlicensed sellers.
-
Enacting Extreme Risk/Red Flag Laws
Prior to the shooting at Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School in Parkland, Florida, on February 14, 2018, nearly 30 people knew about the shooter’s previous violent behavior, and law enforcement groups had been called to incidents involving the shooter on dozens of occasions.1Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School Public Safety Commission. (2019). p. 264, Initial Report Submitted to the Governor, Speaker of the House of Representatives and Senate President. Retrieved from https://www.fdle.state.fl.us/MSDHS/CommissionReport.pdf. This is just one of many examples where a school shooter displayed warning signs of potential violence. States must enact Extreme Risk laws to create a legal process by which law enforcement, family members, and possibly educators can petition a court to temporarily prevent an individual from accessing firearms when there is evidence that they are at serious risk of harming themselves or others. These Extreme Risk protection orders, sometimes also called red flag orders or gun violence restraining orders, provide a way for concerned bystanders to intervene without a criminal proceeding against a potentially dangerous individual. Extreme Risk protection orders include robust due process protections. The court issues final orders after a hearing.
-
Enacting Secure Firearm Storage
Studies show that secure firearm storage laws save lives, particularly by preventing unintentional shootings and firearm suicides. For example, one study found that households that locked both firearms and ammunition had a 78 percent lower risk of self-inflicted firearm injuries and an 85 percent lower risk of unintentional firearm injuries among children and teenagers, compared to those households that left firearms and/or ammunition unlocked.1Grossman, D., & et al. (2005). Gun Storage Practices and Risk of Youth Suicide and Unintentional Firearm Injuries. JAMA, 293(6), 707-714. doi:https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.293.6.707. To protect kids in and out of schools, states must enact and enforce secure firearm storage laws. More than half of states and the District of Columbia currently have some form of secure storage law.2Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2024, January 4). Which states have child-access and/or secure storage laws? Retrieved January 9, 2024, from Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund: https://everytownresearch.org/rankings/law/secure-storage-or-child-access-prevention-required/. In addition, several cities, including New York City and San Francisco, have passed secure storage laws.
-
Raising the Age to Purchase Semi-Automatic Firearms
Under federal law, a person must be 21 years old to purchase a handgun from a licensed gun dealer.118 U.S.C.§ 922(b)(1). However, a person only needs to be 18 years old to purchase that same handgun through an unlicensed sale (such as unlicensed sellers offering guns for sale online or at gun shows) or purchase a rifle or shotgun from a licensed dealer.218 U.S.C.§ 922(b)(1); 18 U.S.C. § 922(x)(2). Research shows that 18- to 20-year-olds commit gun homicides at triple the rate of adults 21 and over.3Everytown Research analysis using FBI Supplementary Homicide Report (SHR) and U.S. Census American Community Survey data 2016–2020. Despite evidence that most perpetrators of school shootings are school-age and have a connection to the school, many states have failed to step in to close these gaps that easily allow firearm access for 18- to 20-year olds.4Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2024, January 4). Has the state raised the minimum age for purchasing firearms? Retrieved January 9, 2024, from Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund: https://everytownresearch.org/rankings/law/minimum-age-to-purchase/; Only six states and DC require a person to be 21 to possess a handgun: DC, DE (beginning in July 2025), IL, MA, MD, NJ, and NY. Only IL and DC require a person to be 21 to possess a rifle or shotgun, and eight states require a person to be 21 to purchase a rifle or shotgun: CA, CO, DE, DC, FL, HI, IL, VT, and WA. At a minimum, states and the federal government must raise the minimum age to 21 years old to purchase or possess handguns and semi-automatic rifles and shotguns to prevent younger shooters from easily obtaining firearms.
-
Keeping Guns Off College Campuses
The vast majority of colleges and universities prohibit guns from being carried on campus, either by state law or school policy. Institutions of higher education have unique risk factors, such as high rates of student mental health challenges and increased use of alcohol and drugs, which make the presence of guns potentially deadly. By contrast, some states require colleges and universities to permit guns to be carried on campus under some circumstances.1Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2024, January 4). Which states don’t force colleges and universities to allow concealed guns on campus? Retrieved from Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund: https://everytownresearch.org/rankings/law/no-guns-mandate-on-college-campuses/.
Supporting the enactment by federal, state, local, territorial, and tribal governments of statutes, rules, and regulations that would prohibit people other than law enforcement agents from possessing firearms on the property of institutions of higher education, the American Bar Association (ABA) noted evidence suggesting that “permissive concealed gun carrying generally will increase crime and place students at risk.” Despite state laws allowing firearms in institutions of higher education, those institutions may still have independent authority to prohibit guns.2American Bar Association. (2023). Report on Resolution 603. Retrieved February 19, 2024, from https://www.americanbar.org/content/dam/aba/directories/policy/midyear-2023/603-midyear-2023.pdf; The American Bar Association (ABA)—citing recent authority holding that new bans on guns on campus should be permitted—highlighted that “a unanimous Montana Supreme Court ruled that state legislators infringed on authority granted to higher education officials by the state constitution by passing a law that permitted open and concealed firearm carrying on university and college campuses. The court declared that ‘maintaining a safe and secure education environment’ fell within the Board of Regents’ purview (and implicitly, that the Board could determine it was necessary to maintain that environment by prohibiting firearms on campus), and recognized that ‘Montana is not immune from the catastrophic loss that follows the use of firearms on school campuses.’” The ABA also called for “states that do not make it unlawful for any person, other than law enforcement, to possess firearms on property owned, operated, or controlled by any public institute of higher education, authorize such institutions of higher education to restrict or regulate the concealed or open carry of firearms on their campuses.”
In states where colleges and universities are required to allow firearms on campus, schools should encourage students to securely store their firearms.
-
Prohibiting Assault Weapons and High-Capacity Magazines
Assault weapons are generally high-powered semi-automatic rifles specifically designed to allow shooters to wound and kill many people quickly. When combined with high-capacity magazines—commonly defined as magazines capable of holding more than 10 rounds of ammunition—a shooter is able to fire more rounds over a short period without pausing to reload. The more rounds a shooter can fire consecutively, the more gunshot wounds they can inflict during an attack. From 2015 to 2022, incidents where individuals used an assault weapon to kill four or more people resulted in 23 times as many people wounded on average compared to those who did not use an assault weapon.1Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2023, May 24). Assault Weapons and High-Capacity Magazines. Retrieved from Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund: https://everytownresearch.org/report/assault-weapons-and-high-capacity-magazines/. Numerous mass shooters in schools, including those responsible for two of the deadliest shootings since 2016, have used assault weapons and high-capacity magazines.2Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund. (2023, May 24). Assault Weapons and High-Capacity Magazines. Retrieved from Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund: https://everytownresearch.org/report/assault-weapons-and-high-capacity-magazines/. NEA and Everytown recommend that states prohibit the possession and sale of assault weapons and magazines capable of holding more than 10 rounds of ammunition.
For more on strategies to advocate for measures that limit access to guns, see NEA’s Legislative Program and Everytown’s Moms Demand Action and Students Demand Action.
Promote Strong Bargaining Language and Administrative Policies
NEA provides guidance on how to secure language regarding aspects of working conditions surrounding gun violence in administrative policies, employee handbooks, and collective bargaining agreements. This bargaining support includes language on:
- Prohibition against arming educators;
- Violence/abuse and threats against educators;
- Support after an assault;
- Broad health and safety provisions for overall safe work environments; and
- Joint health and safety committees.
Promoting Strong Union-Backed Language on School Safety
The San Diego Education Association bargained language on school safety plans that ensures the association is involved in the process of keeping schools safe. The language includes “rules and procedures to be followed by site personnel for their protection, including a method of emergency communication and rules and regulations governing the entering and leaving of school sites.” The language requires that school safety plans explicitly address weapons.1Board of Education of the San Diego Unified School District and the San Diego Education Association. (2022). Collective Bargaining Agreement between the Board of Education, San Diego Unified School District and the San Diego Education Association. Section 11.6.2. Retrieved from https://www.sandiegounified.org/common/pages/DownloadFileByUrl.aspx?key=mIE9NGWW%2b2qmICXsIXIbpHKGrnZf0UAyqh1mqCx7ErAKKj9%2bqmreFSNN4sI84nlgB%2bjcNeICiXuRO6MqgCQkFbLzvlekl8W3c4Po2uQJ7yfkaO7J2tI3DJsoBK%2bz9sx7dCRo9RB8KOEMuabW%2bND0mptkTnI4CKbKnq5Djz9WLHC3S.
In another example, Racine Educators United (REU), in Wisconsin, has aggressively organized around safety concerns in the district, leading, in part, to the creation of the School Safety Committee, an advisory group including five representatives selected by REU and five chosen by the Racine Unified School District (RUSD). Together, REU and RUSD will select parent, student, and community representatives to serve on the committee. The district superintendent also appoints a building services representative. The committee was a settlement of REU grievances and an REU lawsuit against the district.
According to the agreement between REU and RUSD, the School Safety Committee’s review of district policies and procedures will be informed by trauma-sensitive and restorative justice practices and will cover topics including weapons policies, responding to weapons, and gun violence and active shooter response.2Racine Unified School District and Racine Educators United. (2024). Settlement Agreement. Retrieved from https://weac.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/FINAL-CLEAN-Workplace-Safety-Grievances-Settlement-Agreement_.pdf.
Build Strong Partnerships
Addressing gun violence in education settings requires strong, meaningful relationships with partners to deepen association understanding, build relationships, strengthen the processes and policies of Pre-K–12 schools and institutions of higher education, and ensure that approaches developed to keep students, educators, and communities safe are culturally and racially appropriate.
From state to state and within states, potential partners may vary. An important place to start is with other unions representing workers in the Pre-K–12 schools and institutions of higher education where association members work, gun violence-focused organizations, racial and social justice organizations, after-school programs, mental and physical health providers and organizations, associations representing principals or other administrators, and local colleges and universities with programs that identify or address violence in communities or, more specifically, in education settings.
The following list includes several national-level organizations—with links to their websites—that may have state or local counterparts. Identifying local groups working on similar topics may also serve the same purpose.
-
Click to expand this list of national-level organizations
- AAPI Victory Alliance
- AASA—The School Superintendents Association
- Alliance to Reclaim our Schools
- American Academy of Pediatrics
- American Psychological Association
- American School Counselor Association
- Color of Change
- Community Justice Action Fund
- Hope and Heal Fund
- League of United Latin American Citizens
- Life Camp
- Live Free
- March for Our Lives
- MomsRising
- NAACP
- National Association of Elementary School Principals
- National Association of School Nurses
- National Association of School Psychologists
- National Association of Secondary School Principals
- National Association of Social Workers
- National PTA
- National School Boards Association
- Parents Together
- Sandy Hook Promise
- The Trevor Project
- UnidosUS
Engage State Occupational Safety and Health Agencies
State and local associations in any of the 29 states that have created state occupational safety and health agencies can look to the state agency for advocacy and organizing opportunities related to gun violence in Pre-K-12 public schools and public institutions of higher education.55The federal government’s Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) serves to ensure safe and healthy working conditions for the private sector. Federal OSHA does not have jurisdiction over state and local public sector workers. Where established, state agencies are required by federal law to be at least as effective as OSHA in protecting workers and in preventing work-related injuries, illnesses, and deaths.
In states with a safety and health agency covering public employees but without a workplace violence standard, the association or an individual member can file a complaint if workplace conditions are unsafe. Workplace violence standards allow for the association and members to be involved in the development and review of worksite violence plans. The state of New York has established a workplace violence prevention standard applicable to public schools,56New York State. (2024). Retrieved from Workplace Violence Prevention Information: https://dol.ny.gov/workplace-safety. and California is developing one.
Promote Professional Development, Capacity-Building, and Staffing
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and U.S. Department of Education have awarded $1.5 billion in short-term grants for school safety, improved access to mental health services, and support for young people to address trauma and grief from gun violence. The U.S. Department of Justice has awarded an additional $60 million in short-term grants. The Bipartisan Safer Communities Act (BSCA) commits to expanding the pipeline by designating $500 million for training to increase the pool of skilled professionals providing mental health services in schools.
In early 2024, Vice President Harris announced an additional $285 million in funding for schools to hire and train mental health counselors.57Psychiatrist.com. (2024, January 15). “Vice President Harris Announces New Funding for Mental Health Professionals in Schools. Psychiatrist.com. Retrieved from https://www.psychiatrist.com/news/vice-president-harris-announces-new-funding-for-mental-health-professionals-in-schools/. Grants are not meant to be the long-term solution, but they can assist school districts with infrastructure needs and the ability to hire and train counselors, psychologists, social workers, and other mental health professionals. To identify funding opportunities for mental health support in education settings, see NEA’s webpage on school-based mental health services grants. In addition, explore whether state-mandated professional development for educators includes trainings on suicide prevention, trauma-informed crisis intervention, de-escalation techniques, restorative practices, and trauma-informed strategies.
Get Involved in Local Government
Educators play an essential role in the communities in which they work. The experience they’ve gained while working with students gives them a unique perspective when it comes to making public education policy, negotiating collective bargaining agreements, and setting budget priorities for their communities.
Gun Violence Prevention Resources
-
National Education Association Resources
- National Education Association: The National Education Association is the nation’s largest union, representing more than 3 million elementary and secondary teachers, higher education faculty, education support professionals, specialized instructional support personnel, school administrators, retired educators, and students preparing to become educators.
- NEA Health and Safety Program: NEA School Health and Safety provides information and solutions related to student and educator mental health, violence prevention and response, infection control, and environmental and occupational safety and health, among other topics.
- Bargaining and Advocacy Tactics to End Gun Violence: NEA provides advocates in bargaining and non-bargaining statute states with sample language to secure in board policies, employee handbooks, and collective bargaining agreements regarding aspects of working conditions surrounding gun violence.
- Gun Violence Prevention Measures Using the Hierarchy of Controls: To help address this worsening public health crisis, employers and educators can implement the hierarchy of controls—a proven approach to minimize or eliminate exposure to workplace hazards—to sensibly prevent gun violence in education contexts.
- NEA School Crisis Guide: Produced in 2018, the guide provides detailed content on how to effectively prevent, prepare for, respond to, and recover from school crises.
- Responding to Gun Violence: This portion of the NEA Health and Safety Program website provides content on taking action, helping students cope, resources for school leaders, fostering mental health, and preventing hate and bias, as well as resources for school leaders.
- We Can Change This: Educators Take on Gun Violence: Educators across the country are working to end the era of school shootings that has defined students’ lives.
- NEA Legislative Program: The National Education Association’s Legislative Program encapsulates NEA’s priorities for advocating in Congress for federal laws that support public K-12 schools and postsecondary institutions, student learning, and educators
Mental Health Supports:
- Bargaining and Advocacy Tactics to Support Educators’ Mental Health: This resource compiles strategies to improve mental health support for educators using collective bargaining or advocacy.
- The Bipartisan Safer Communities Act: The Bipartisan Safer Communities Act unlocks more than $1 billion additional funding for mental health and other services.
- NEA Member Benefits Mental Health Program: Through NEA Member Benefits, in partnership with AbleTo, NEA members receive no-cost access to evidence-backed tools for stress, anxiety, depression, and other mental health needs.
- School-Based Mental Health Services Grants: NEA provides a summary of federal grant programs that support efforts to increase school-based mental health services and programs.
Safe and Supportive Schools:
- Addressing the Epidemic of Trauma in Schools: This report builds a framework to advance trauma awareness and trauma-informed approaches, including some currently being implemented by NEA state affiliates. It includes key recommendations for ways in which NEA may address the trauma crisis through policy, programs, and practices. It also includes a list of selected resources developed or suggested as references by affiliates to address student and educator trauma.
- Cultural Competence Training: Through NEA’s Cultural Competence Training Program, NEA members learn how to become culturally competent educators.
- How Restorative Practices Work for Students and Educators: This NEA Today article explores what happens in public schools where educators care more about creating a community built upon kindness, not consequences.
- How to Be an Advocate for Students Who Are Bullied: These recommendations support educators in helping students who are bullied.
- How to Identify Bullying: This article provides tips for addressing bullying.
- NEA Micro-Credential Courses on Restorative Practices: Each of the five micro-credentials in this stack can stand alone or be completed sequentially: Exploring Restorative Practices; Building a Positive Classroom Community with Affective Language; Restorative Circles—Building Relationships in the Classroom; Restorative Conferencing; and Implementing Restorative Practices.
- NEA Micro-Credential Course on Trauma-Informed Pedagogy: This course addresses child trauma, how trauma affects the brain, trauma-informed pedagogy, leveled intervention strategies, behavioral support plans, replacement behaviors, and teaching students to self-advocate.
- Restorative Practices: Fostering Healthy Relationships and Promoting Positive Discipline in Schools—A Guide for Educators: This guide helps educators better understand what restorative practices are and how they can foster safe learning environments through community building and constructive conflict resolution.
- Supporting the Advocacy, Communication, and Implementation of Life Skills in Public Schools: A Toolkit: Social-emotional learning (SEL)—also known as positive youth development or life skills—is widely supported by families, students, and educators and provides valuable skills and lessons that contribute to students’ success throughout their lives.
- Tools and Tips for Trauma-Informed Practices: Educators in every school community can use these practices to create safe and supportive learning environments for their students.
- Trauma-Informed Schools: Supporting students who suffer from childhood trauma requires whole-school involvement and transformation. The NEA and its affiliates are actively engaged in finding ways for schools and educators to address the issue of trauma and its implications for learning, behavior, and school safety.
Community Engagement and Dialogue:
- Community Schools: Community schools are public schools that provide services and support that fit each neighborhood’s needs, created and run by the people who know our children best.
- Strategies for Effective Health and Safety Dialogue: This NEA training module will help support families, educators, and students effectively communicate around health and safety issues.
-
Everytown Resources
- Everytown for Gun Safety: Everytown for Gun Safety is the largest gun violence prevention organization in America. The organization is a movement of more than 10 million supporters working to end gun violence.
- Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund: The Everytown Support Fund is the education, research, and litigation arm of Everytown for Gun Safety. It seeks to improve our understanding of the causes of gun violence and help to reduce it by conducting ground-breaking original research, developing evidence-based policies, communicating this knowledge to the American public, and advancing gun safety and gun violence prevention in communities and the courts.
- Be SMART: The Be SMART program focuses on fostering conversations with other adults about secure gun storage. In this context, the acronym stands for Secure guns in homes and vehicles, Model responsible behavior, Ask about unsecured guns in homes, Recognize the role of guns in suicide, and Tell your peers to be SMART. The program’s purpose is to facilitate behavior change for adults and help parents and adults prevent child gun deaths and injuries.
- City Dashboard: Gun Homicide: The FBI is the leading source of city gun violence data across the country, covering more than 94 percent of the U.S. population in 2022. Everytown’s City Gun Homicide dashboard allows users to explore gun homicide trends across more than 500 cities with populations of 65,000+ that reported data to the FBI from 2018 to 2022.
- CityGRIP—Safe Passage: Safe passage programs provide safe routes to and from schools to reduce student exposure to gun violence. To achieve this goal, educators, law enforcement groups, and communities collaboratively implement protocols and procedures to ensure student safety.
- Community-Led Public Safety Strategies: For decades, community-based organizations have successfully reduced violence by implementing alternative public safety measures that are locally driven and informed by data. Often referred to as violence intervention programs, these strategies have expanded greatly over the years and include street outreach, group violence intervention, crime prevention through environmental design, hospital-based violence intervention programs, safe passage programs, and cognitive behavioral therapy.
- EveryStat: EveryStat is a one-stop source for gun violence in your state and county, including breakdowns by intent, race and ethnicity, gender, economic cost, and more.
- Everytown Gun Law Rankings: Everytown compares gun policy across the country and scores every state on the strength of its gun law and compares it with its rate of gun violence.
- Everytown Law Fund: Everytown Law Fund provides support for impact litigation to advance the right of every person to be free from gun violence and to speak, work, learn, pray, assemble, protest, and vote without fear or intimidation.
- Everytown Survivor Network: The Everytown Survivor Network is a nationwide community of survivors working together to end gun violence. The network amplifies the power of survivor voices, offers trauma-informed programs, provides information on direct services, and supports survivors in their advocacy.
- Extreme Risk/Red Flag Laws: Extreme Risk laws, sometimes referred to as “red flag” laws, allow loved ones or law enforcement to intervene by petitioning a court for an order to temporarily prevent someone in crisis from accessing guns.
- Gunfire on School Grounds: The database details the myriad ways in which gun violence manifests in U.S. schools.
- Mayors Against Illegal Guns: Mayors Against Illegal Guns is a coalition of mayors fighting to end gun violence by working to fight for gun safety laws and enact gun violence prevention strategies.
- Moms Demand Action: Moms Demand Action, a part of Everytown for Gun Safety, is the nation’s largest grassroots volunteer network that is working to end gun violence. The organization campaigns for new and stronger solutions to lax gun laws and loopholes that jeopardize the safety of families, educates policymakers and parents about the importance of secure firearm storage, and works to create a culture of gun safety through partnerships with businesses, community organizations, and influencers. There is a Moms Demand Action chapter in every state and more than 700 local groups throughout the country.
- One Thing You Can Do: This database includes information about extreme risk orders by state. An extreme risk order is a way to intervene when there is reason to believe a loved one is at serious risk of harming themselves or others.
- Students Demand Action: Students Demand Action is the largest grassroots, youth-led gun violence prevention group in the country, with more than 800 groups and active volunteers in every state and the District of Columbia. The movement, created by and for teens and young adults, aims to channel the energy and passion of high school and college-age students into the fight against gun violence.
Other Resources
-
Safe and Supportive School Climates
- Bullying Prevention: From the National Association of School Psychologists, this site provides resources to prevent bullying.
- Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design: From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) focuses on principles to create safer schools by developing environments that promote positive behavior and reduce opportunities for violence to occur.
- Guiding Principles for Creating Safe, Inclusive, Supportive, and Fair School Climates: From the U.S. Department of Education’s Office of Planning, Evaluation, and Policy Development, this document recommends evidence-based practices that schools and school districts can take to implement fair student discipline approaches, which keep students safely in learning environments and help to address disproportionality in discipline and exclusion.
- National Center on Safe Supportive Learning Environments: From the National Center on Safe and Supportive Schools, this site offers information and technical assistance to states, districts, schools, institutions of higher education, and communities focused on improving school climate and conditions for learning.
- The National Technical Assistance Center on Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports: The center provides information, tools, and technical assistance for implementing Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS), a tiered framework for supporting students’ behavioral, academic, social, emotional, and mental health. These resources include guides, lesson plans, assessment surveys, and examples of how to integrate trauma-informed practices into PBIS.
- Resources for Educators: From Sandy Hook Promise, this site provides resources on multiple topics.
- Schoolsafety.gov: This interagency website created by the federal government provides a broad range of information, resources, and guidance to create safe and supportive learning environments for students and educators.
-
Mental Health Supports
- 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline: The 988 Lifeline provides 24/7, free and confidential support for people in distress, prevention and crisis resources for you or your loved ones, and best practices for professionals in the United States.
- Emotional CPR: Emotional CPR (eCPR) is an educational program designed to teach people to assist others through an emotional crisis by implementing three simple steps: C = Connecting; P = emPowering; and R = Revitalizing.
- Mental Health First Aid: Mental Health First Aid is an evidence-based, early intervention course that teaches participants about mental health and substance use challenges.
- The Mental Health Technology Transfer Center Network: Funded by SAMHSA, the center develops resources, disseminates information, and provides training and technical assistance to mental health work, including a free online course for educators on mental health literacy.
- Project Aware: Through SAMHSA, Project Aware (Advancing Wellness and Resiliency in Education) promotes a sustainable infrastructure for school-based mental health programs and services. AWARE grantees build collaborative partnerships with the state education agency, local education agency, tribal education agency, the state mental health agency, community-based providers of behavioral health care services, school personnel, community organizations, families, and school-age youth.
- Screen4Success: Screen4Success is a screening tool to identify areas where someone may benefit from more support on personal health, wellness, and well-being. It also provides local and national resources to help address those concerns. You can use the tool for self-screening, or you can send it to someone you are concerned about. You can also help that person fill out the screener—this provides opportunities for discussion in the moment—or they can complete it on their own if that’s not possible.
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) National Helpline: SAMHSA’s National Helpline, 1-800-662-HELP (4357) (also known as the Treatment Referral Routing Service), or TTY: 1-800-487-4889 is a confidential, free, 24-hour-a-day, 365-day-a-year information service, available in English and Spanish, for individuals and family members facing mental and/or substance use disorders. This service provides referrals to local treatment facilities, support groups, and community-based organizations. The site also includes additional resources.
Navigate to Other Sections of the Guide
Everytown Research & Policy is a program of Everytown for Gun Safety Support Fund, an independent, non-partisan organization dedicated to understanding and reducing gun violence. Everytown Research & Policy works to do so by conducting methodologically rigorous research, supporting evidence-based policies, and communicating this knowledge to the American public.
In partnership with
-
![]()
NEA
The National Education Association (NEA) is more than 3 million people—educators, students, activists, workers, parents, neighbors, and friends—who believe in the opportunity for all students and the power of public education to transform lives and create a more just and inclusive society. NEA has affiliate organizations in every state and more than 14,000 communities across the United States. NEA’s vision for safe, just, and equitable schools consists of thriving spaces that are safe and welcoming for all students; are discriminatory toward none; integrate the social, emotional, physical, mental, and spiritual needs of the whole student; and equitably and fully fund the community school model with wraparound services and resources. The resources in this guide can help make this vision a reality.


